TUTORIALS | TYPES OF PHOTOGRAPHY | TIPS AND TRICKS
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT PHOTOGRAPHY
1. CAMERA PARTS AND FUNCTIONS
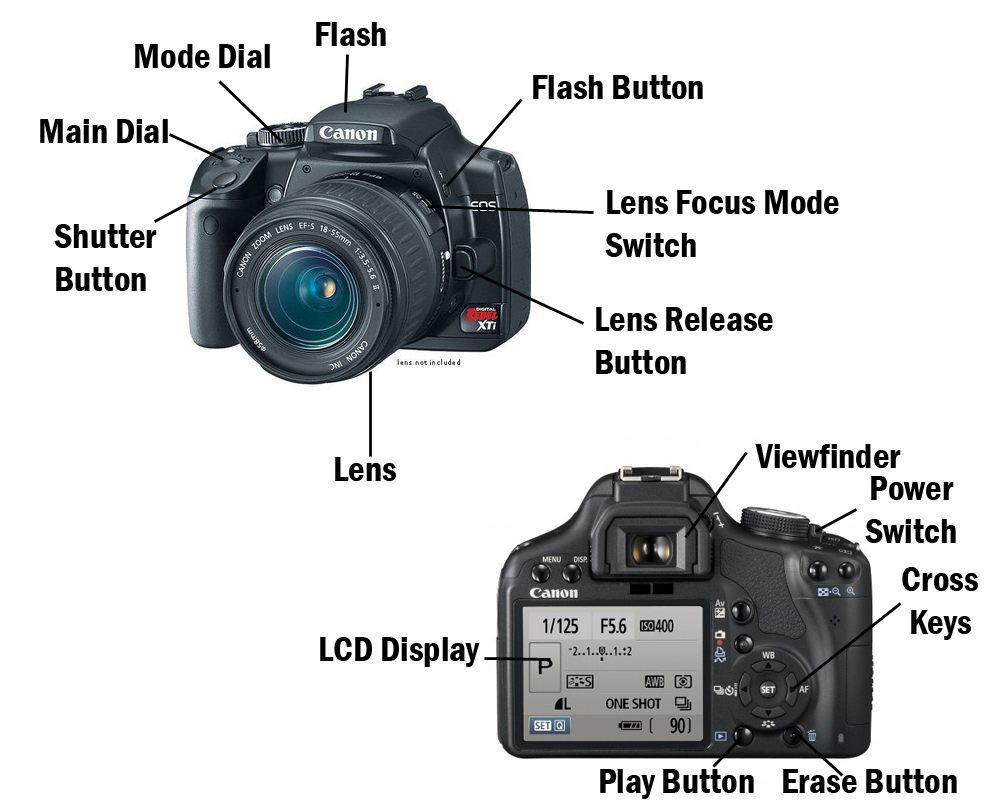
Disclaimer: The figure above is a Canon camera parts and functions. Camera buttons and functions may vary from other camera brands.
2. THE EXPOSURE TRIANGLE: APERTURE, ISO and SHUTTER SPEED

APERTURE
APERTURE: The higher the aperture, the more background will
be visible. If the aperture is lower, the background will be
blurred.
*Keep in mind that the lower the aperture, the more expensive the
lens will be.
SHUTTER SPEED
SHUTTER SPEED: A fast shutter speed means that less light is
entering your camera, while a slow shutter speed means that more
light is entering your camera.
*A fast shutter speed is recommended for morning photoshoots,
while a slow shutter speed is recommended for night photoshoots.
ISO
ISO: ISO in a camera refers to the sensitivity of the
camera's image sensor to light. It is an important camera setting
that determines how much light is needed to produce a properly
exposed photo. A higher ISO setting makes the camera's sensor more
sensitive to light, allowing for photos to be taken in low-light
conditions without the need for a slower shutter speed or wider
aperture. However, increasing the ISO also increases the amount of
digital noise in the image, which can result in a loss of detail and
image quality. Therefore, photographers typically choose an ISO
setting that balances the need for a well-exposed image with the
desire for high-quality results.
*I highly recommend to keep your ISO low to avoid grainy pictures.
TYPES OF PHOTOGRAPHY
1. PORTRAIT PHOTOGRAPHY
One of the most common photography styles, portrait photography, or
portraiture, aims to capture the personality and mood of an
individual or group.
Images may be candid or posed, full body or close-ups. Either way,
the subject’s face and eyes are typically in focus. Lighting and
backdrop help to convey tone and emotion.
Popular types of photography portraits include senior portraits,
family portraits, engagement photos, and professional headshots.
The best portrait photographers make clients feel completely
comfortable, so that their expressions are natural and relaxed.

2. PHOTOJOURNALISM
Photojournalism is a way of telling the story of a newsworthy
(perhaps even historic) event or scene through photographs.
Photojournalism should be as objective and truthful as possible and
capturing candid moments as they happen is more important than
getting picture-perfect shots.
Generally, photojournalists attend planned events with the hope of
capturing unplanned, unscripted moments. Their work is routinely
published in magazines and newspapers.
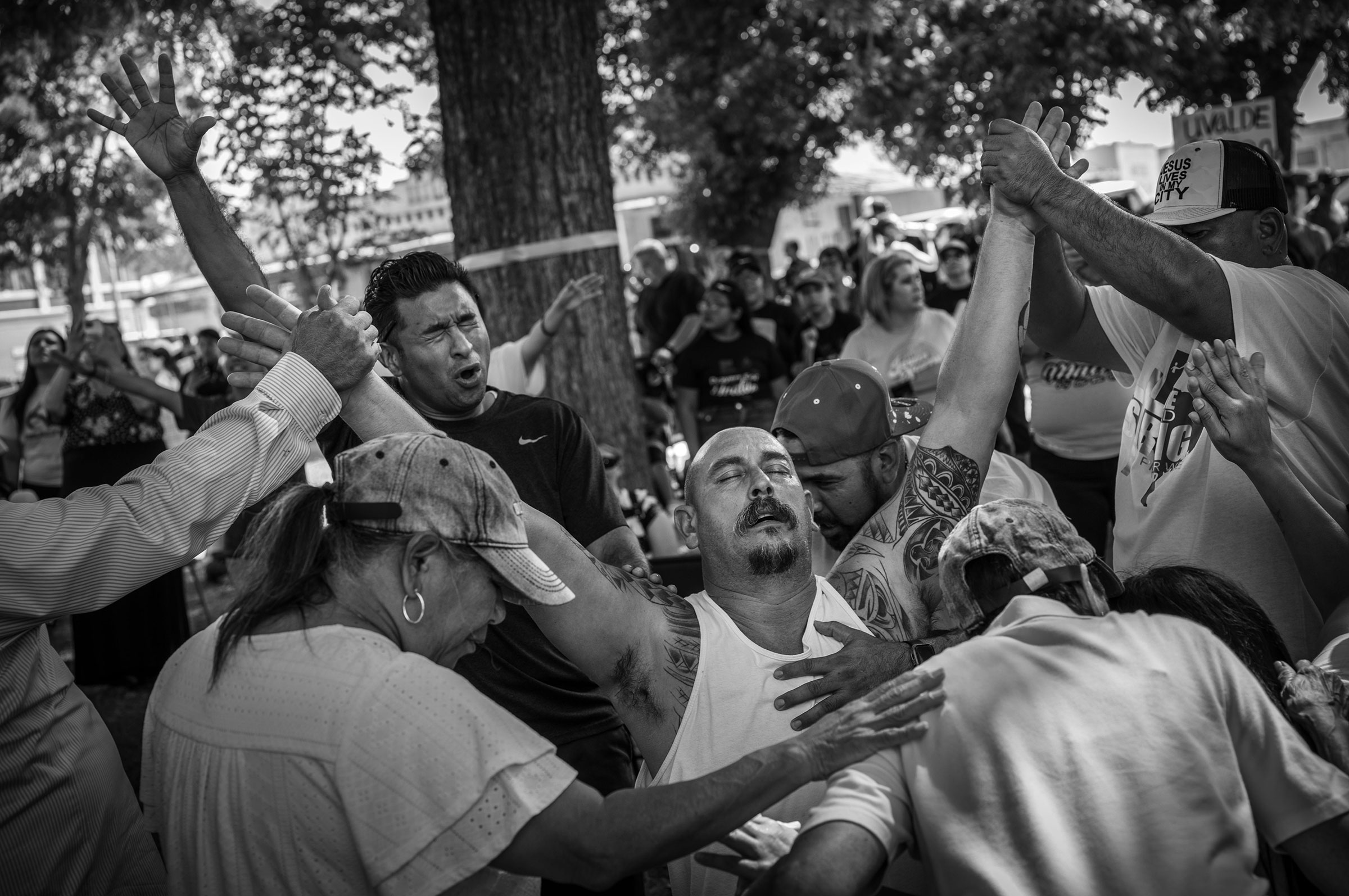

3. SPORTS PHOTOGRAPHY
By catching athletes, coaches, and even fans at the perfect moment,
sports photographs can depict the passion, drama, and emotion that
fuels sporting events.
Sports photographers must aim and shoot quickly to keep up with the
action around them, and it’s best practice to use a higher ISO to
shoot at a faster shutter speed.
Sports photographers also usually use long, heavy lenses for zooming
in on the action. Interesting angles can help make your work stand
out in this competitive genre.

4. ARCHITECTURAL PHOTOGRAPHY
Both the interior and exterior design of buildings and structures
are the subject of architectural photography.
From warehouses to city bridges to old country barns, this genre
encompasses diverse structures. Often, the photograph showcases the
structure’s most aesthetically pleasing parts, such as a particular
beam or archway.
Interesting materials and colors may also be emphasized.
Lighting can be challenging in architectural photography and, for
exteriors, photographers must know how to work with natural light.
Gear such as a tilt-shift lens, a tripod, and a panorama head is
often useful. Architectural photographs can be of value to
designers, architects, leasing companies, and building investors.

TIPS AND TRICKS FOR BEGINNERS
1. LEARN THE BASICS
It's important to understand the basics of photography, such as aperture, shutter speed, ISO, composition, and lighting. There are plenty of resources online, such as tutorials, books, and courses that can help you learn these fundamental concepts.
2. EXPERIMENT
Don't be afraid to experiment with your camera settings, angles, and composition. This is how you can discover your personal style and develop your own creative vision.
3. PRACTICE REGULARLY
The more you practice, the better you'll get. Take your camera with you wherever you go and try to capture interesting subjects and compositions. Regular practice will help you hone your skills and develop your own unique style.
4. LEARN FROM OTHERS
Look at the work of other photographers for inspiration and ideas. Analyze their techniques and compositions to gain insight into how they create their images.
5. DON'T RELY ON GEAR
While having good equipment can certainly help, it's important to remember that the best camera won't make up for poor technique or composition. Focus on developing your skills first and then invest in gear that will help you achieve your goals.
6. KEEP IT SIMPLER
In the beginning, it's easy to get overwhelmed by all the different settings and options on your camera. Start by keeping it simple and focusing on one or two settings at a time. This will help you develop a deeper understanding of each setting and how it affects your photos.
7. HAVE FUN
Photography is a fun and rewarding hobby, so don't forget to enjoy the process! Experiment, try new things, and don't be afraid to make mistakes. The more you enjoy the process, the more likely you are to stick with it and improve over time.